温度適応の多様性を引き起こす適応回路ダイバーシティー /Adaptive circuit diversity causing natural variation in temperature acclimation

久原 篤 /Atsushi Kuhara
甲南大学理工学部 / 統合ニューロバイオロジー研究所 教授
Konan University, Faculty of Science and Engineering / Institute for Integrative Neurobiology, Professor
HPリンク
研究室HP:http://kuharan.com/index.html/
リサーチマップ:https://researchmap.jp/atsushi_kuhara//
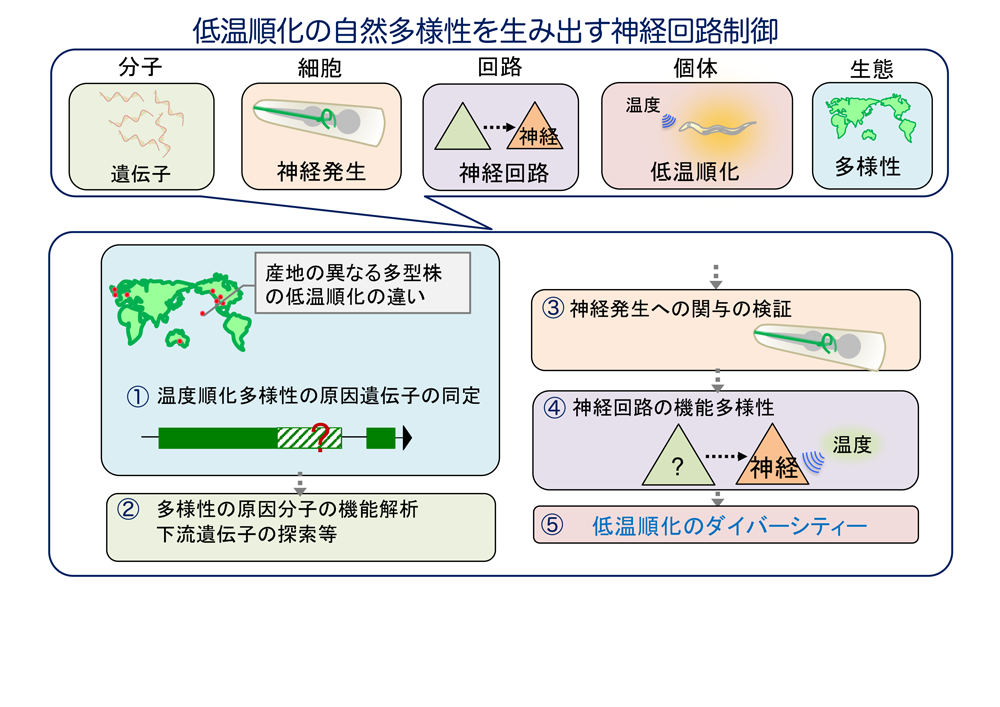
温度は地球上において必ず存在する環境情報であり、動物の個体の温度応答に関わる温度受容体として、皮膚や神経系で発現するサーモTRPチャネルや、線虫では独自に同定した温度受容体DEG/ENcCや温度受容体GPCRが存在する。それらの温度受容体が受け取った温度情報が伝達される末梢神経系から中枢までの神経回路は比較的同定されてきている。その一方で、動物が変動する温度環境下において、暴露された温度環境に徐々に一定の時間をかけて慣れていく温度順化に関わる神経変遷機構には未知の点が残されている。本研究では、環境温度に徐々に慣れていく温度順化の違いが、動物種の温度適応の多様性に重要であると考え、神経活動イメージングやトランスクリプトーム解析に長けている実験動物である線虫C.elegansを使い、産地の異なるC.elegansが示す低温順化の多様性を引き起こす神経回路と、その作動原理を解き明かすことを目的とし解析を進める。具体的には、低温順化の多様性に関わる原因遺伝子が、温度順化の多様性を引き起こす際に、どのような分子に対してどのようなタイミングで作用するのかを明らかにしする。さらに、どの神経回路が低温順化多様性を作り出すのかを同定し、低温順化の多様性を引き起こす神経活動の違いを神経活動イメージングで定量化する。以上の解析から、低温順化の多様性に伴い進化の過程で選択・機能構築されてきた神経回路の多様性を明らかにする。
文献
- Ohnishi K et al. (2024) G protein-coupled receptor-based thermosensation determines temperature acclimatization of Caenorhabditis elegans.
Nature commun., 15: 1660, 1-13. - Motomura H et al. (2022) Head-tail-head neural wiring underlies gut fat storage in Caenorhabditis elegans temperature acclimation.
PNAS, 119, 32, e2203121119, 1-9. - Takagaki N et al. (2020) The mechanoreceptor DEG-1 regulates cold tolerance in Caenorhabditis elegans.
EMBO reports, 21, e48671, 1-14. - Okahata M et al. (2019) Cold acclimation via the KQT-2 potassium channel is modulated by oxygen in Caenorhabditis elegans.
Science Advances, 5, 2, 1-12.